How is cyber-resilience defined and measured?
Cyber Resilience
Cyber Resilience Defined
Resilience testing, also known as cybersecurity
testing or red teaming, involves simulating real-world cyber attacks to evaluate the organization's
ability to detect, respond, and recover from such incidents. The focus is on assessing the organization's
resilience against different types of threats, including social engineering, phishing, network breaches,
and more. The testing is performed by skilled cybersecurity professionals who act as adversaries,
attempting to exploit vulnerabilities and weaknesses within the organization's systems and defenses.
The results help identify gaps in security controls, incident response capabilities, and overall cyber
resilience, allowing organizations to strengthen their defenses and response strategies.
Cyber-resilience is becoming a popular
term in the cyber security business and is defined as the ability of an enterprise to limit the
impact of security attacks. Focusing on cyber-resilience is part of a broader approach to digital
risk management that aims to not only defend against cyber-attacks, but also ensure that the enterprise
is able to survive and recover quickly following an attack.

-
-
How are breach risk and cyber-resilience related?
-
What is the best way to improve cyber-resilience for your enterprise?
Why Cyber Resilience Is Important
A cyber resilience strategy is vital for business continuity. It can provide benefits beyond increasing an enterprise's security posture and reducing the risk of exposure to its critical infrastructure. Cyber resilience also helps reduce financial loss and reputational damage. And if an organization receives cyber resilience certification, it can instill trust in its clients and customers. Further, a cyber-resilient company can optimize the value it creates for its customers, increasing its competitive advantage through effective and efficient operations.

Effective cyber resilience also involves governance, risk management, an understanding of data ownership and incident management.
-
Cyber resilience services
-
Data security solutions
-
Incident response solutions
How does cyber resilience work?
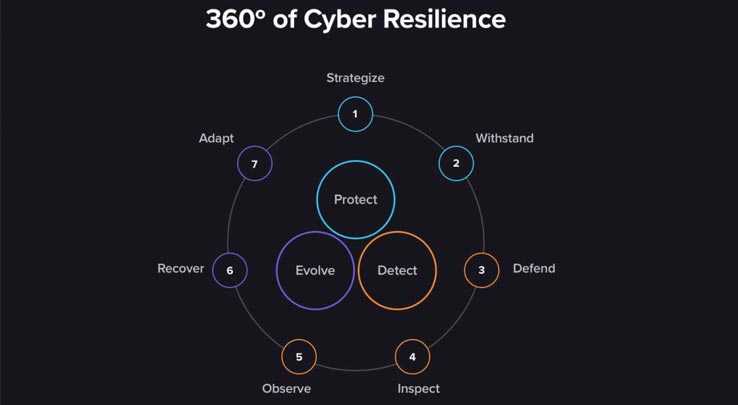
Cyber resilience can be understood through a lifecycle based on the stages of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) service lifecycle: strategy, design, transition, operation and improvement.
-
Cyber resilience strategy:
Based on the organization's objectives, strategy work identifies critical assets, such as information, systems and services that matter most to it and its stakeholders. This work also includes identifying vulnerabilities and the risks they face. -
Cyber resilience transition:
Transition work from design to operational use tests controls and refines incident detection to identify when critical assets are under stress from internal, external, intentional or accidental action. -
Cyber resilience operation:
Operational work controls and detects and manages cyber events and incidents, including continual control testing to ensure effectiveness, efficiency and consistency. -
Cyber resilience evolution:
Evolution work continually protects an ever-changing environment. As organizations recover from incidents, they must learn from the experiences, modifying their procedures, training, design and even strategy..
How can cyber resilience be improved?
An effective cyber resiliency strategy will include components of multiple cybersecurity solutions. These include:
-
Data security
-
Application security
-
Identity and access management
-
Security operations

